Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases...Read more
Temporary disability can happen to anyone at any time, and it’s important to understand the laws that protect workers in these situations. When an employee is unable to work due to an injury or illness, temporary disability benefits may be available to help them cover their expenses and maintain financial stability. However, navigating the legal framework around these benefits can be confusing, so it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what laws apply to temporary disability in the workplace.
In this article, we’ll explore the various laws and regulations that govern temporary disability at work. From the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) to state-specific disability laws, we’ll break down the key provisions and requirements that employees and employers need to know. Whether you’re facing a temporary disability or managing employees who are, understanding these laws can help you navigate this challenging time with confidence.
What Laws Apply to Temporary Disability at the Workplace?
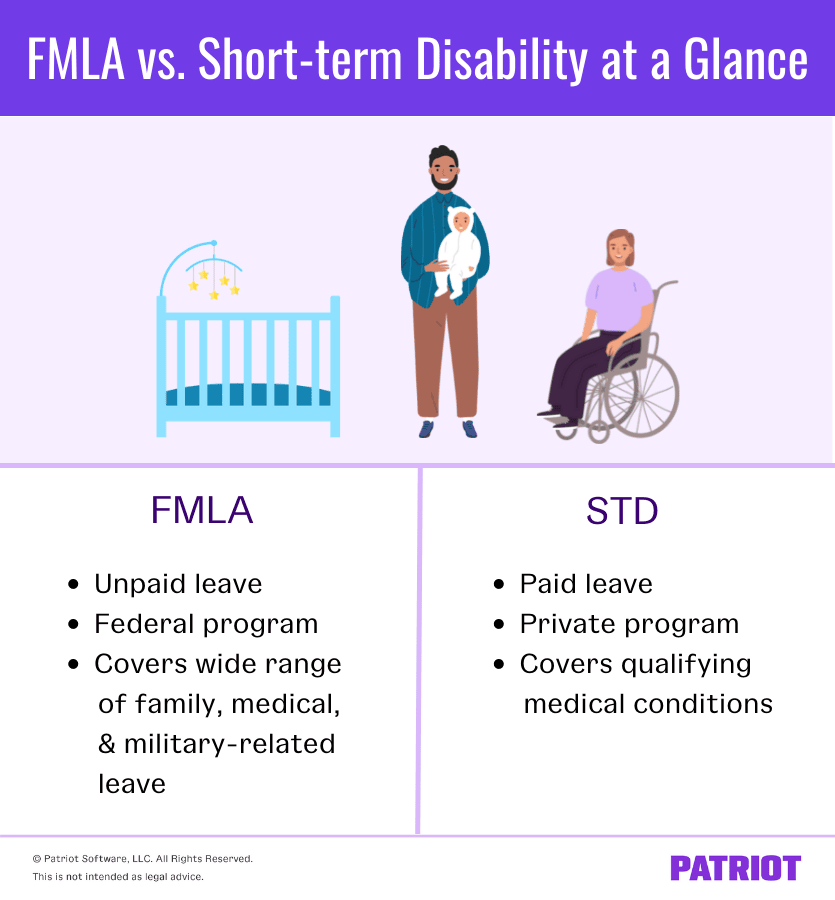
Temporary disability at the workplace is covered under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA). The ADA prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities, including temporary disabilities, and requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations. The FMLA provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave for a serious health condition, including temporary disabilities. Additionally, some states have their own temporary disability insurance programs that provide benefits to employees who are unable to work due to a temporary disability.
Contents
- Understanding the Laws that Apply to Temporary Disability at the Workplace
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is temporary disability?
- What laws protect employees with temporary disabilities?
- What are an employer’s obligations to accommodate an employee with a temporary disability?
- What is an employee’s obligation to inform their employer of a temporary disability?
- What can an employee do if they believe their employer is not complying with applicable laws related to temporary disability?
- Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
Understanding the Laws that Apply to Temporary Disability at the Workplace
Temporary disability is a common occurrence in the workplace, and it can be caused by various factors such as accidents, illnesses, or injuries. When an employee is unable to work due to temporary disability, employers have a legal obligation to provide accommodations and support. In this article, we will discuss the laws that apply to temporary disability at the workplace and what employers and employees should know.
What is Temporary Disability?
Temporary disability is a condition where an employee is unable to work due to a medical condition. This can be caused by an injury or illness that is not permanent but requires the employee to take time off work to recover. Temporary disability can also be caused by pregnancy-related medical conditions or mental health conditions that require time off work.
Types of Temporary Disability
Temporary disability can be categorized into two types: total and partial. Total temporary disability means that the employee is completely unable to work due to their medical condition. Partial temporary disability means that the employee is still able to work but is limited in their ability to perform certain tasks.
Legal Protections for Employees with Temporary Disability
Employees with temporary disability are protected by several laws, including the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA). The ADA requires employers to provide reasonable accommodations to employees with disabilities, including those with temporary disabilities. The FMLA allows eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period to recover from a serious health condition or to care for a family member with a serious health condition.
Employer Responsibilities for Employees with Temporary Disability
Employers have several responsibilities when it comes to employees with temporary disability. These include providing reasonable accommodations, allowing employees to take time off work, and not discriminating against employees with disabilities.
Reasonable Accommodations
Employers are required to provide reasonable accommodations to employees with disabilities, including those with temporary disabilities. Reasonable accommodations can include modifying work hours, providing a modified work schedule, or providing assistive technology.
Time off Work
Employers are required to allow employees to take time off work to recover from a temporary disability. This can include providing paid sick leave or allowing employees to take unpaid leave under the FMLA.
Non-Discrimination
Employers are not allowed to discriminate against employees with disabilities, including those with temporary disabilities. This includes not denying employment, promotions, or training opportunities based on an employee’s disability.
Employee Rights for Temporary Disability
Employees with temporary disability have several rights, including the right to reasonable accommodations, the right to take time off work, and the right to not be discriminated against.
Reasonable Accommodations
Employees with temporary disability have the right to request reasonable accommodations from their employer. This can include modifications to their work schedule or the use of assistive technology.
Time off Work
Employees with temporary disability have the right to take time off work to recover from their medical condition. This can include taking paid sick leave or taking unpaid leave under the FMLA.
Non-Discrimination
Employees with temporary disability have the right to not be discriminated against based on their medical condition. This includes not being denied employment, promotions, or training opportunities based on their disability.
Benefits of Supporting Employees with Temporary Disability
Supporting employees with temporary disability can have several benefits for employers, including increased productivity, reduced absenteeism, and improved employee morale.
Increased Productivity
Providing reasonable accommodations and allowing employees to take time off work can help employees with temporary disability recover faster and return to work sooner, which can increase productivity.
Reduced Absenteeism
Employees who feel supported and accommodated by their employer are less likely to miss work due to their medical condition, which can reduce absenteeism.
Improved Employee Morale
Employers who support employees with temporary disability can improve employee morale and create a more positive work environment. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and employee retention.
Temporary Disability vs. Permanent Disability
There are several differences between temporary disability and permanent disability. Temporary disability is a medical condition that is not permanent and allows the employee to return to work once they have recovered. Permanent disability is a medical condition that is permanent and prevents the employee from returning to work in their previous capacity.
Differences in Legal Protections
Employees with permanent disability are protected by several laws, including the ADA and the Rehabilitation Act. These laws provide additional protections for employees with permanent disabilities, including accommodations for job training and job placement.
Differences in Employer Responsibilities
Employers have different responsibilities when it comes to employees with permanent disability. These include providing reasonable accommodations, making physical modifications to the workplace, and providing job training and job placement services.
Differences in Employee Rights
Employees with permanent disability have different rights than employees with temporary disability. These rights include the right to receive accommodations for job training and job placement and the right to not be discriminated against based on their disability.
In conclusion, understanding the laws that apply to temporary disability at the workplace is important for both employers and employees. Employers have a legal obligation to provide accommodations and support for employees with temporary disability, and employees have the right to request reasonable accommodations and take time off work to recover. By supporting employees with temporary disability, employers can increase productivity, reduce absenteeism, and improve employee morale, creating a more positive work environment for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
Temporary disability is a common workplace issue that can affect anyone. To help you understand your rights and obligations, here are some frequently asked questions about the laws that apply to temporary disability at the workplace.
What is temporary disability?
Temporary disability is a condition that affects an employee’s ability to perform their job duties for a limited period of time. This may be due to an illness or injury that is not permanent, but requires the employee to take time off work or perform modified duties. Examples of temporary disabilities include broken bones, surgery recovery, severe flu, or pregnancy-related complications.
Temporary disability can be caused by a workplace accident or an outside injury or illness. It is important for employers to have policies in place to support employees with temporary disabilities, and for employees to understand their rights and responsibilities in these situations.
What laws protect employees with temporary disabilities?
Several laws protect employees with temporary disabilities in the workplace. These include the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), and state laws related to disability and leave. The ADA prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities, including temporary disabilities, and requires employers to make reasonable accommodations to enable employees to perform their job duties. The FMLA provides eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave per year for certain medical and family reasons, including temporary disability.
State laws may provide additional protections, such as paid leave or job protection for employees with temporary disabilities. Employers should consult with legal counsel to ensure compliance with all applicable laws.
What are an employer’s obligations to accommodate an employee with a temporary disability?
An employer has an obligation to provide reasonable accommodations to enable an employee with a temporary disability to perform their job duties. Accommodations may include modified work hours, modified duties, or assistive devices or technology. Employers should engage in an interactive process with the employee to identify and implement appropriate accommodations.
However, an employer is not required to provide accommodations if doing so would cause an undue hardship, such as significant expense or disruption to the business. Employers should consult with legal counsel to determine what accommodations are appropriate and reasonable in a given situation.
What is an employee’s obligation to inform their employer of a temporary disability?
An employee has an obligation to inform their employer of a temporary disability as soon as possible. This allows the employer to make necessary accommodations and plan for the employee’s absence or modified duties. Failure to inform the employer may result in disciplinary action or loss of benefits, such as leave or disability pay.
Employees should provide their employer with a doctor’s note or other documentation to support their need for accommodations or leave related to a temporary disability. This documentation should include the expected duration of the disability and any necessary accommodations or restrictions.
If an employee believes their employer is not complying with applicable laws related to temporary disability, they may file a complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) or a state agency responsible for enforcing these laws. Employees may also consult with legal counsel to determine their options and potential remedies.
It is important for employees to understand their rights and options in these situations, and to document any incidents or communication related to their temporary disability and accommodations.
In conclusion, understanding the laws that apply to temporary disability at the workplace is crucial for both employers and employees. Employers have a legal obligation to provide reasonable accommodations to employees with temporary disabilities, while employees have the right to request such accommodations without fear of discrimination or retaliation. It is important for both parties to communicate effectively and work together to ensure that employees with temporary disabilities are able to perform their job duties and participate fully in the workplace.
Moreover, employers should familiarize themselves with federal and state laws governing temporary disability, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), to ensure that they are in compliance and avoid potential legal disputes. Additionally, employers should provide training to their managers and supervisors on how to handle requests for accommodations and how to support employees with temporary disabilities.
Finally, employees should be aware of their rights and responsibilities when it comes to temporary disability at the workplace. They should communicate openly with their employers about their needs and work with them to develop reasonable accommodations that will allow them to perform their job duties to the best of their abilities. By working together, employers and employees can create a more inclusive and productive workplace for everyone.
Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases from minor injuries to devastating accidents, earning him a sterling reputation as a trusted and passionate advocate for justice. Brenton's unwavering dedication to his clients has cemented his position as a sought-after personal injury attorney.
- Latest Posts by Brenton Armour
-
Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- -
South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- -
Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
- All Posts