Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases...Read more
Have you ever been diagnosed with a mental health condition only to find that the treatment isn’t working? Misdiagnosis is a common problem in the field of mental health, especially for Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD). In fact, studies show that up to 70% of individuals with BPD are initially misdiagnosed.
Misdiagnosis can have serious consequences, including prolonged suffering, inappropriate treatment, and even worsening of symptoms. This is why it’s essential to understand what misdiagnosis for BPD is, why it happens, and how to prevent it. In this article, we’ll explore these issues in detail, providing you with the knowledge you need to take control of your mental health.
Contents
- What is Misdiagnosis for BPD?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common misdiagnoses for BPD?
- What are the consequences of misdiagnosis for BPD?
- What can be done to prevent misdiagnosis of BPD?
- How can patients advocate for themselves to prevent misdiagnosis of BPD?
- What are the best treatments for BPD?
- Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
What is Misdiagnosis for BPD?
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that affects approximately 1.6% of the adult population. Unfortunately, it is often misdiagnosed due to its many overlapping symptoms, which can lead to ineffective treatment and a prolonged period of suffering. In this article, we will explore the common misdiagnoses for BPD and how to identify them.
1. Mood Disorders
Mood disorders such as depression and bipolar disorder share many symptoms with BPD, including emotional instability, impulsivity, and self-harm. However, the key difference is the underlying cause of these symptoms. In BPD, the emotional instability is a core feature of the disorder, whereas in mood disorders, it is a symptom of an underlying chemical imbalance.
Misdiagnosis can result in ineffective treatment, as the medications used to treat mood disorders are unlikely to address the core symptoms of BPD. It is essential that mental health professionals consider all symptoms and their root causes before making a diagnosis.
2. PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is another condition that shares symptoms with BPD, including anxiety, dissociation, and self-harm. However, PTSD is caused by a traumatic event, whereas BPD is a personality disorder.
Misdiagnosis can occur when a mental health professional focuses on the trauma history and overlooks other symptoms that are unrelated to PTSD. It is important to note that trauma can play a role in the development of BPD, but it is not the sole cause.
3. Substance Abuse Disorders
Substance abuse disorders and BPD are often comorbid, meaning they occur together. However, the symptoms of substance abuse can mask the symptoms of BPD, leading to misdiagnosis.
It is crucial for mental health professionals to assess for both substance abuse and BPD to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Treating only the substance abuse without addressing the underlying BPD can result in relapse and continued suffering.
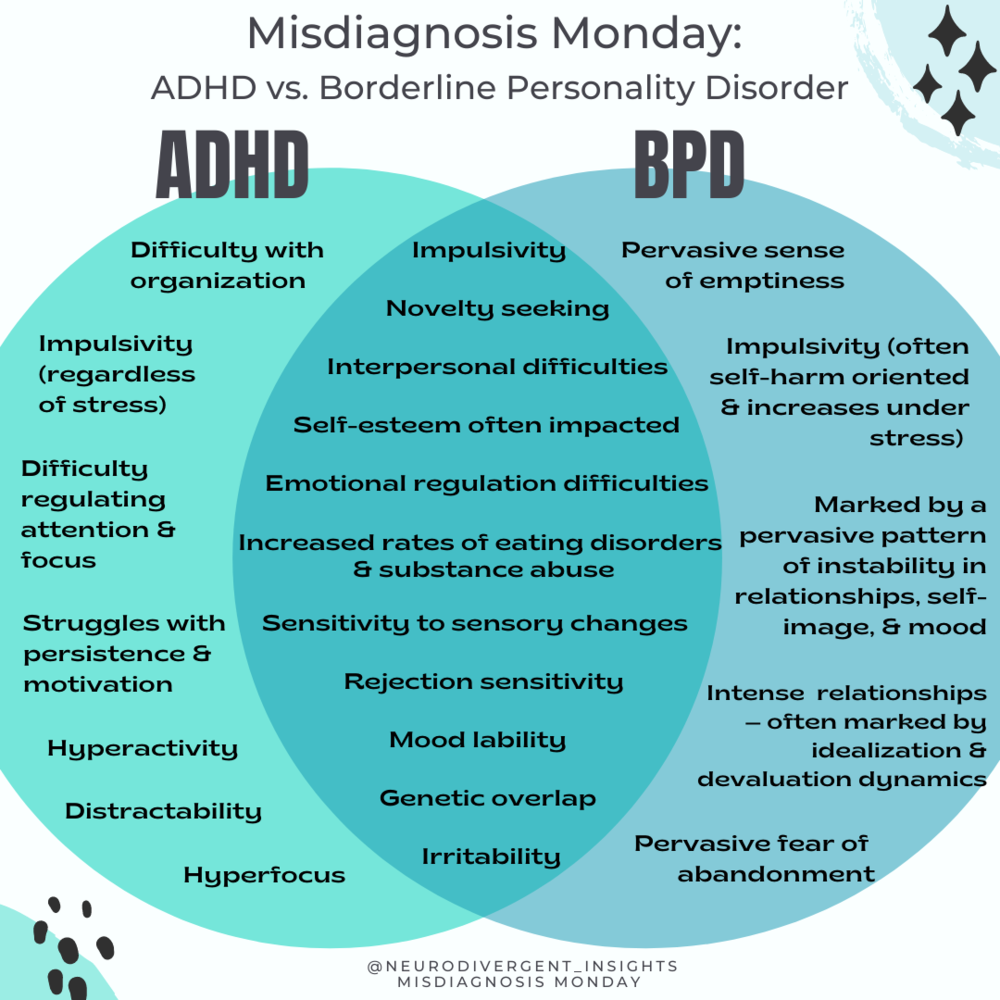
4. ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and BPD share symptoms such as impulsivity and mood swings. However, ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder, whereas BPD is a personality disorder.
Misdiagnosis can occur when the mental health professional focuses on the impulsivity and overlooks the emotional instability and self-harm that are core features of BPD. It is important to consider all symptoms and their underlying causes before making a diagnosis.
5. Avoidant Personality Disorder
Avoidant Personality Disorder (AvPD) and BPD share symptoms such as fear of abandonment and social isolation. However, the key difference is the motivation behind these symptoms. In AvPD, the fear of rejection and criticism is the primary driver, whereas in BPD, it is the fear of abandonment.
Misdiagnosis can result in ineffective treatment, as the therapies used for AvPD may not address the core symptoms of BPD. It is important to assess for all symptoms and their underlying causes to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
6. Narcissistic Personality Disorder
Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD) and BPD share symptoms such as a need for attention and admiration. However, the key difference is the motivation behind these symptoms. In NPD, the need for attention and admiration is driven by a sense of superiority and entitlement, whereas in BPD, it is driven by a fear of abandonment.
Misdiagnosis can result in ineffective treatment, as the therapies used for NPD may not address the core symptoms of BPD. It is essential to assess for all symptoms and their underlying causes to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Antisocial Personality Disorder (ASPD) and BPD share symptoms such as impulsivity and a history of criminal behavior. However, the key difference is the motivation behind these symptoms. In ASPD, the behavior is driven by a disregard for the rights of others, whereas in BPD, it is driven by emotional dysregulation and fear of abandonment.
Misdiagnosis can result in ineffective treatment, as the therapies used for ASPD may not address the core symptoms of BPD. It is important to assess for all symptoms and their underlying causes to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
8. Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia and BPD share symptoms such as paranoia and dissociation. However, the key difference is the underlying cause of these symptoms. In schizophrenia, the symptoms are caused by a chemical imbalance in the brain, whereas in BPD, they are caused by emotional dysregulation.
Misdiagnosis can occur when a mental health professional focuses on the symptoms and overlooks the emotional instability and fear of abandonment that are core features of BPD. It is crucial to assess for all symptoms and their underlying causes to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
9. Benefits of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of BPD is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes. With an accurate diagnosis, mental health professionals can tailor treatment to address the core symptoms of the disorder, including emotional instability, fear of abandonment, and self-harm.
Effective treatment can lead to improved relationships, increased self-awareness and self-esteem, and reduced symptoms. Accurate diagnosis can also reduce the stigma associated with BPD and increase access to appropriate treatment.
10. Conclusion
Misdiagnosis of BPD is common due to its many overlapping symptoms with other mental health conditions. It is crucial for mental health professionals to assess for all symptoms and their underlying causes to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Accurate diagnosis can lead to improved outcomes and reduced stigma associated with BPD.
Frequently Asked Questions
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that can be difficult to diagnose. Misdiagnosis of BPD can lead to ineffective treatment and potential harm to the patient. Here are some frequently asked questions about misdiagnosis for BPD:
What are the common misdiagnoses for BPD?
There are several mental health conditions that share similar symptoms with BPD, which can lead to misdiagnosis. Some of the most common misdiagnoses for BPD include bipolar disorder, depression, anxiety disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Bipolar disorder can be misdiagnosed as BPD because both conditions share symptoms such as mood swings, impulsivity, and reckless behavior. Depression and anxiety disorders can also be mistaken for BPD because they can cause similar symptoms, such as mood changes and difficulty regulating emotions. PTSD can be misdiagnosed as BPD because both conditions can cause intense emotions and difficulty with relationships.
What are the consequences of misdiagnosis for BPD?
Misdiagnosis of BPD can have serious consequences for the patient. If a patient is misdiagnosed with a different condition, they may receive inappropriate treatment that does not address their underlying issues. This can lead to a worsening of symptoms and potentially harmful side effects from medication.
In addition, misdiagnosis can delay the proper diagnosis and treatment of BPD, which can have long-term effects on the patient’s mental health and well-being. Without proper treatment, BPD can lead to significant impairment in relationships, work, and other areas of life.
What can be done to prevent misdiagnosis of BPD?
Preventing misdiagnosis of BPD requires careful assessment and evaluation by a qualified mental health professional. This may involve a comprehensive psychological evaluation, including interviews with the patient and their family members or loved ones.
It is also important for mental health professionals to be aware of the common misdiagnoses for BPD and to carefully consider all possible diagnoses before making a final determination. Collaboration with other healthcare providers, such as primary care physicians and psychiatrists, can also help to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How can patients advocate for themselves to prevent misdiagnosis of BPD?
Patients can advocate for themselves by being open and honest with their healthcare providers about their symptoms and experiences. It can be helpful to keep a journal or record of symptoms and to bring this to appointments with mental health professionals.
In addition, patients can ask questions about the diagnostic process and the rationale behind any diagnoses that are given. It is important for patients to be actively involved in their own care and to feel empowered to ask for a second opinion if they are unsure about a diagnosis.
What are the best treatments for BPD?
The best treatments for BPD are those that are evidence-based and tailored to the individual needs of the patient. This may include psychotherapy, medication, and other forms of support such as group therapy or peer support.
Psychotherapy, particularly dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), has been shown to be effective in treating BPD. Medications such as mood stabilizers or antipsychotics may also be used to address specific symptoms, such as mood swings or impulsivity. It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a treatment plan that is effective and appropriate for their individual needs.
In conclusion, misdiagnosis of borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a common problem that can lead to significant negative consequences for patients. Due to the complexity of the disorder and its symptoms, it can often be mistaken for other mental health conditions, such as depression or bipolar disorder. This misdiagnosis can result in delayed or ineffective treatment, and may even worsen the patient’s condition.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be trained in recognizing the signs and symptoms of BPD in order to provide accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. This includes taking a thorough patient history, conducting a comprehensive mental health assessment, and utilizing evidence-based diagnostic criteria.
Patients with BPD need tailored treatment approaches that address their unique symptoms and challenges. Misdiagnosis can prevent them from receiving the care they need, leading to further distress and potential harm. By improving awareness and understanding of BPD among healthcare providers, we can work towards reducing misdiagnosis and improving outcomes for those living with this complex disorder.
Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases from minor injuries to devastating accidents, earning him a sterling reputation as a trusted and passionate advocate for justice. Brenton's unwavering dedication to his clients has cemented his position as a sought-after personal injury attorney.
- Latest Posts by Brenton Armour
-
Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- -
South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- -
Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
- All Posts