Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases...Read more
In today’s globalized world, it’s not uncommon for American companies to have operations in multiple countries. But what happens when it comes to federal laws? Does U.S. law apply to non-American workplaces? It’s a complex and often confusing issue that can have significant legal consequences for both employers and employees. In this article, we’ll explore the nuances of federal law and its application in non-American workplaces, and what it means for businesses operating on a global scale. So, let’s dive in and find out what the law says.
Federal law generally does not apply to non-American workplaces. However, U.S. employers with foreign operations must still comply with local laws, and some U.S. laws, such as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, do have extraterritorial reach. Additionally, U.S. citizens working abroad for U.S. employers may still be covered by certain federal laws, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act and the Family and Medical Leave Act.
Contents
- Does Federal Law Apply to Non American Workplaces?
- Overview of Federal Labor Laws
- The Extraterritorial Application of Federal Law
- The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
- Other Federal Laws and Non-American Workplaces
- The Benefits of Federal Law in Non-American Workplaces
- The Risks of Non-Compliance with Federal Law
- The Vs of Following Federal Law in Non-American Workplaces
- The Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Does federal law apply to non-American workplaces?
- 2. Can American employees sue their employers for violations of U.S. law in non-American courts?
- 3. What are the consequences for American companies that violate non-American laws?
- 4. Can American companies be sued in U.S. courts for violations of non-American laws?
- 5. What can American employees and companies do to protect themselves when working abroad?
- Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
Does Federal Law Apply to Non American Workplaces?
Federal law is a complex and ever-changing field that governs many aspects of American life. But what happens when an American employee is working outside of the United States? Does federal law still apply, or are they subject to the laws of the country in which they are working? In this article, we will explore the question of whether federal law applies to non-American workplaces.
Overview of Federal Labor Laws
Federal labor laws are designed to protect the rights of American workers and ensure that they are treated fairly by their employers. These laws cover a wide range of issues, including minimum wage, overtime pay, workplace safety, discrimination, and more. Some of the most important federal labor laws include the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), the Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA), and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
The Extraterritorial Application of Federal Law
One of the key questions when it comes to federal law and non-American workplaces is whether federal law has extraterritorial application. In other words, can federal law apply to American employees who are working outside of the United States? The answer is that it depends on the specific law in question.
For example, the FLSA applies to all employees who are engaged in interstate commerce or the production of goods for interstate commerce. This means that if an American employee is working for a company that engages in interstate commerce, even if they are working outside of the United States, they are still covered by the FLSA. Similarly, OSHA applies to all American employees, regardless of where they are working.
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) is another federal law that has extraterritorial application. The FCPA is designed to prevent American companies from bribing foreign officials in order to gain a business advantage. The law applies to all American companies, as well as any foreign companies that do business in the United States.
Under the FCPA, American employees who are working outside of the United States are still subject to the law. This means that if an American employee bribes a foreign official in order to gain a business advantage, they can be prosecuted under the FCPA, even if the bribery occurred outside of the United States.
Other Federal Laws and Non-American Workplaces
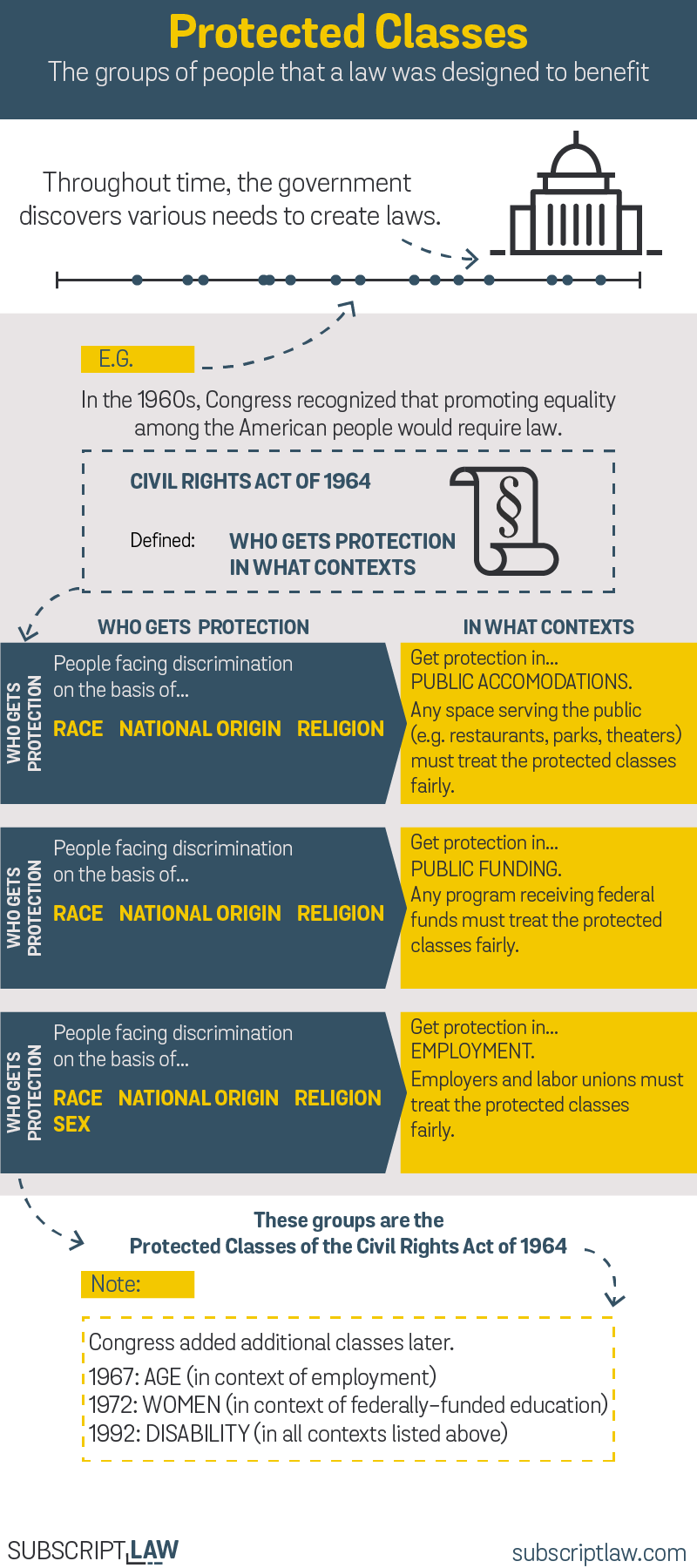
While some federal laws have extraterritorial application, others do not. For example, the ADA only applies to American employers with 15 or more employees, and only applies to American employees who are working within the United States. Similarly, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits workplace discrimination based on race, sex, religion, and other factors, only applies to American employers with 15 or more employees, and only applies to American employees who are working within the United States.
The Benefits of Federal Law in Non-American Workplaces
While federal law may not apply to all American employees who are working outside of the United States, there are still benefits to having federal law as a guidepost. For example, many American companies have policies that apply globally, regardless of the local laws in the country in which their employees are working. These policies may be based on federal law, and can help to ensure that American employees are treated fairly and consistently, even when working in a foreign country.
The Risks of Non-Compliance with Federal Law
American companies that operate globally need to be aware of the risks of non-compliance with federal law. Even if federal law does not have extraterritorial application, American companies can still face legal and financial consequences for violating federal laws. For example, if an American employee working outside of the United States is not paid minimum wage or overtime as required by the FLSA, the company can still face penalties and lawsuits.
The Vs of Following Federal Law in Non-American Workplaces
While it can be challenging to navigate the complex web of federal and foreign laws that apply to non-American workplaces, there are many benefits to following federal law. By doing so, American companies can ensure that their employees are treated fairly and consistently, regardless of where they are working. This can help to build a positive reputation for the company, and can also help to minimize legal and financial risks.
The Conclusion
In conclusion, federal law does have extraterritorial application in some cases, but not in others. American employees who are working outside of the United States need to be aware of the specific federal laws that apply to their situation, as well as any foreign laws that may also apply. By following federal law, American companies can ensure that their employees are treated fairly and consistently, and can avoid legal and financial risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about whether federal law applies to non-American workplaces.
1. Does federal law apply to non-American workplaces?
The short answer is no. Federal law only applies to workplaces within the United States and its territories. Non-American workplaces are subject to the laws of the country in which they are located. However, there are some exceptions to this rule. For example, U.S. anti-discrimination laws may apply to American employees working for American companies abroad, and U.S. labor laws may apply to American companies that operate abroad.
It is important for American employees working abroad and American companies operating abroad to understand the laws that apply to them. They should consult with legal experts who are familiar with the laws of the country in which they are located and with U.S. laws that may apply to them.
2. Can American employees sue their employers for violations of U.S. law in non-American courts?
It depends on the circumstances and the laws of the country in which the employee is working. In some cases, American employees may be able to sue their employers for violations of U.S. law in non-American courts. For example, if an American employee is working in a country that has a treaty with the United States that allows for the enforcement of U.S. judgments in that country, the employee may be able to sue their employer in that country. However, if there is no such treaty, the employee may need to bring their lawsuit in U.S. courts.
It is important for American employees working abroad to understand their legal rights and the options available to them for enforcing those rights. They should consult with legal experts who are familiar with the laws of the country in which they are located and with U.S. laws that may apply to them.
3. What are the consequences for American companies that violate non-American laws?
The consequences for American companies that violate non-American laws depend on the laws of the country in which the violation occurred. In some cases, the company may be subject to fines or other penalties imposed by the foreign government. In other cases, the company may face civil lawsuits brought by individuals who were harmed by the violation. In extreme cases, the company may be barred from doing business in the country where the violation occurred.
It is important for American companies operating abroad to understand the laws that apply to them and to comply with those laws. They should consult with legal experts who are familiar with the laws of the country in which they are operating and with U.S. laws that may apply to them.
4. Can American companies be sued in U.S. courts for violations of non-American laws?
It depends on the circumstances and the laws of the country in which the violation occurred. In some cases, American companies may be sued in U.S. courts for violations of non-American laws. For example, if the company is accused of violating a treaty that the United States has with the country where the violation occurred, the company may be sued in U.S. courts. However, if there is no such treaty, the company may need to defend itself in the courts of the country where the violation occurred.
It is important for American companies operating abroad to understand the legal risks they face and to take steps to minimize those risks. They should consult with legal experts who are familiar with the laws of the country in which they are operating and with U.S. laws that may apply to them.
5. What can American employees and companies do to protect themselves when working abroad?
American employees and companies can take several steps to protect themselves when working abroad. First, they should understand the laws that apply to them in the country where they are located. They should consult with legal experts who are familiar with those laws and with U.S. laws that may apply to them. Second, they should establish clear policies and procedures for complying with those laws. Finally, they should train their employees to understand and comply with those policies and procedures.
By taking these steps, American employees and companies can minimize their legal risks and ensure that they are operating in compliance with applicable laws.
In conclusion, the question of whether federal law applies to non-American workplaces is a complex and nuanced one. While the general rule is that U.S. laws do not apply outside of the country’s borders, there are exceptions to this rule that can make it difficult to determine when and where federal law applies.
One such exception is the extraterritorial application of certain laws, such as those related to anti-corruption or securities fraud. Additionally, some U.S. laws may apply to foreign workplaces if they involve U.S. citizens or companies, or if they have a significant impact on U.S. interests.
Ultimately, the application of federal law to non-American workplaces requires a case-by-case analysis and legal expertise. Employers with operations outside of the U.S. should consult with experienced legal counsel to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases from minor injuries to devastating accidents, earning him a sterling reputation as a trusted and passionate advocate for justice. Brenton's unwavering dedication to his clients has cemented his position as a sought-after personal injury attorney.
- Latest Posts by Brenton Armour
-
Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- -
South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- -
Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
- All Posts