Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases...Read more
Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer that affects men, particularly those over the age of 50. While early detection and treatment can significantly improve the chances of survival, there are growing concerns about the accuracy of prostate cancer diagnoses. Recent studies suggest that misdiagnosis of prostate cancer is becoming more common, raising questions about the effectiveness of current screening methods.
Despite advances in medical technology and increased awareness of prostate cancer, misdiagnosis remains a significant concern. In this article, we will explore the reasons behind the rising rates of misdiagnosis, the potential consequences for patients, and what can be done to improve accuracy in prostate cancer diagnosis.
There has been an increase in the diagnosis of prostate cancer in recent years, which may lead to an increased risk of misdiagnosis. Some factors that contribute to misdiagnosis include the use of PSA testing, which has a high rate of false positives, and a lack of clear guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. It is important for patients to discuss the risks and benefits of testing with their healthcare provider and to seek a second opinion if they are unsure about their diagnosis.
Contents
- Are There Increases in Misdiagnosis of Prostate Cancer?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the common methods used to diagnose prostate cancer?
- What are the factors contributing to the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer?
- Are there increases in the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer?
- What are the potential harms of overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer?
- What can be done to reduce the misdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer?
- Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
Are There Increases in Misdiagnosis of Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer among men. In recent years, there has been growing concern about the accuracy of prostate cancer diagnoses. Misdiagnosis can have serious consequences, including unnecessary treatment or delayed treatment that can result in a worse prognosis. In this article, we will explore the issue of misdiagnosis of prostate cancer and examine whether there have been increases in recent years.
What is Prostate Cancer?
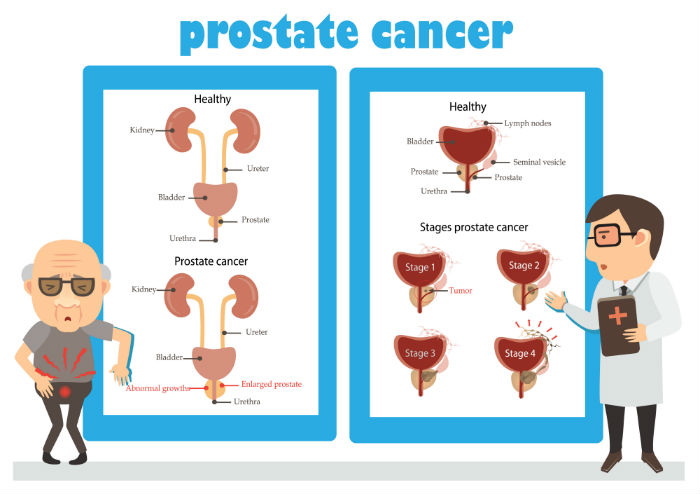
The prostate is a gland located in the male reproductive system. It is responsible for producing fluid that forms part of semen. Prostate cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the prostate gland grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a tumor. It is the second most common cause of cancer deaths among men in the United States.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
There are several risk factors associated with prostate cancer, including age, family history, and race. Men over the age of 50 are at higher risk of developing prostate cancer, while men with a family history of the disease are also more likely to develop it. African-American men are also at higher risk of developing prostate cancer than men of other races.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer often does not cause any symptoms. As the cancer grows, it can cause a range of symptoms, including difficulty urinating, frequent urination, blood in the urine or semen, and pain in the back, hips, or pelvis. However, these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, making it difficult to diagnose prostate cancer based solely on symptoms.
The Issue of Misdiagnosis
Misdiagnosis occurs when a patient is given an incorrect diagnosis of a medical condition. In the case of prostate cancer, misdiagnosis can occur in several ways. For example, a patient may be diagnosed with prostate cancer when they do not have the disease, or they may be told they do not have cancer when they actually do.
Causes of Misdiagnosis of Prostate Cancer
There are several factors that can contribute to the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer. One common cause is the use of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. While the PSA test can help detect prostate cancer, it is not always accurate and can produce false-positive results. This can lead to unnecessary biopsies and treatment.
Another factor that can contribute to misdiagnosis is the interpretation of biopsy results. Biopsies involve taking a sample of tissue from the prostate gland and examining it for cancer cells. However, the interpretation of biopsy results can be subjective, and there can be a risk of missing cancerous cells.
Have There Been Increases in Misdiagnosis?
There is evidence to suggest that misdiagnosis of prostate cancer may be increasing in recent years. One study published in the Journal of Urology found that the rate of misdiagnosis in men with prostate cancer increased from 7.8% in 1986 to 21.6% in 1991. Other studies have also reported increasing rates of misdiagnosis in recent years.
Possible Reasons for the Increase in Misdiagnosis
There are several possible reasons why misdiagnosis of prostate cancer may be increasing. One factor is the widespread use of PSA testing, which can lead to overdiagnosis and unnecessary treatment. Another factor is the increasing use of imaging tests, which can detect small tumors that may not require treatment.
Benefits and Risks of PSA Testing
PSA testing can be useful in detecting prostate cancer in its early stages, which can increase the chances of successful treatment. However, there are also risks associated with PSA testing, including false-positive results, overdiagnosis, and unnecessary treatment. It is important for patients to discuss the benefits and risks of PSA testing with their doctor and make an informed decision about whether to undergo the test.
Conclusion
In conclusion, misdiagnosis of prostate cancer is a serious issue that can have significant consequences for patients. While there is evidence to suggest that misdiagnosis may be increasing, there are steps that can be taken to improve the accuracy of diagnoses, such as improving the interpretation of biopsy results and reducing the use of unnecessary tests and treatments. Patients should also be aware of the risks and benefits of PSA testing and make informed decisions about their health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men, and it is important to diagnose it early for better treatment outcomes. However, there have been concerns about the accuracy of prostate cancer diagnosis, leading to questions about whether there are increases in misdiagnosis.
What are the common methods used to diagnose prostate cancer?
The most common methods used to diagnose prostate cancer are a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test. If either of these tests shows abnormalities, a biopsy is usually performed to confirm the diagnosis. However, these tests are not always accurate, and there are concerns about overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer.
Overdiagnosis occurs when prostate cancer is diagnosed and treated, even though it would not have caused any harm if left untreated. Overtreatment occurs when men with low-risk prostate cancer receive aggressive treatments that may have serious side effects, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
What are the factors contributing to the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer?
There are several factors that can contribute to the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer. One of the main factors is the inaccuracy of the PSA test, which can result in false positives and false negatives. Another factor is the interpretation of biopsy results, which can be subjective and may lead to overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
Other factors include the lack of consensus on the definition of clinically significant prostate cancer, the variability in biopsy techniques and pathology interpretation, and the influence of financial incentives on diagnosis and treatment decisions.
Are there increases in the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer?
There is some evidence to suggest that there may be increases in the misdiagnosis of prostate cancer. One study found that up to 50% of men with prostate cancer may be overdiagnosed, leading to unnecessary treatment. Another study found that the accuracy of the PSA test may be declining over time, leading to more false positives and false negatives.
However, it is important to note that not all experts agree on the extent of misdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer. Some argue that the benefits of early detection and treatment outweigh the harms, particularly for men at high risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
What are the potential harms of overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer?
The potential harms of overdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer include unnecessary biopsies, surgeries, radiation therapy, and other treatments that may have serious side effects, such as urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, and bowel problems. These treatments can also be costly and may cause psychological distress for patients and their families.
Furthermore, overdiagnosis and overtreatment can divert resources away from more pressing health issues and may lead to a false sense of security among men who believe they are protected from prostate cancer when they are not.
What can be done to reduce the misdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer?
To reduce the misdiagnosis and overtreatment of prostate cancer, experts recommend a more personalized approach to diagnosis and treatment, taking into account each patient’s individual risk factors and preferences. This may involve using more accurate tests, such as MRI and genomic testing, to better distinguish between clinically significant and insignificant prostate cancer.
Other strategies include improving the quality and consistency of biopsy techniques and pathology interpretation, increasing public awareness of the risks and benefits of prostate cancer screening, and reducing financial incentives for overdiagnosis and overtreatment.
In conclusion, the issue of misdiagnosis of prostate cancer is a complex one that requires more attention and research. While improvements in diagnostic tools have led to better detection of the disease, they have also led to an increase in the number of false positives. This, in turn, can lead to unnecessary treatment and anxiety for patients. It is important that healthcare professionals stay informed about the latest developments in diagnostic tools and guidelines, in order to minimize the risk of misdiagnosis and ensure that patients receive appropriate care.
Furthermore, patient education and awareness are crucial in preventing misdiagnosis. Men should be encouraged to seek regular check-ups and discuss any concerns with their healthcare providers. They should also be aware of the potential risks and benefits of different diagnostic tests and treatment options, so that they can make informed decisions about their health.
Finally, more research is needed to determine the factors contributing to misdiagnosis of prostate cancer and to identify strategies for improving accuracy and reducing the risk of false positives. By working together, healthcare professionals, patients, and researchers can help ensure that men receive the best possible care for this common and potentially deadly disease.
Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases from minor injuries to devastating accidents, earning him a sterling reputation as a trusted and passionate advocate for justice. Brenton's unwavering dedication to his clients has cemented his position as a sought-after personal injury attorney.
- Latest Posts by Brenton Armour
-
Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- -
South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- -
Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
- All Posts