Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases...Read more
Giving birth is an incredible and life-changing experience, but unfortunately, it can also be a time of great risk. One of the most devastating outcomes of childbirth is brain injury, which can lead to lifelong challenges for infants and their families. What causes brain injury at birth, and what can be done to prevent it? In this article, we’ll explore the various factors that can contribute to this serious condition, from medical complications to environmental factors, and highlight the steps that healthcare providers and parents can take to minimize the risk of injury and ensure the best possible outcomes for newborns.
What Causes Brain Injury at Birth?
Brain injury at birth can occur due to various reasons such as a difficult or prolonged delivery, oxygen deprivation, premature birth, infections, and maternal health issues. Lack of oxygen to the brain during birth is a common cause of brain injury and can lead to conditions like cerebral palsy, developmental delays, and seizures. Proper medical care during pregnancy and labor can help prevent brain injury at birth.
Contents
- What Causes Brain Injury at Birth?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the most common causes of brain injury at birth?
- What are the signs and symptoms of brain injury at birth?
- How is brain injury at birth diagnosed?
- What are the treatment options for brain injury at birth?
- What is the long-term outlook for babies with brain injury at birth?
- Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
What Causes Brain Injury at Birth?
Brain injury at birth can be a devastating condition that affects both the child and their family. It can result in long-term physical, cognitive, and behavioral disabilities, and can often require ongoing medical care and support. Understanding the causes of brain injury at birth is essential to preventing it from happening and improving outcomes for affected children.
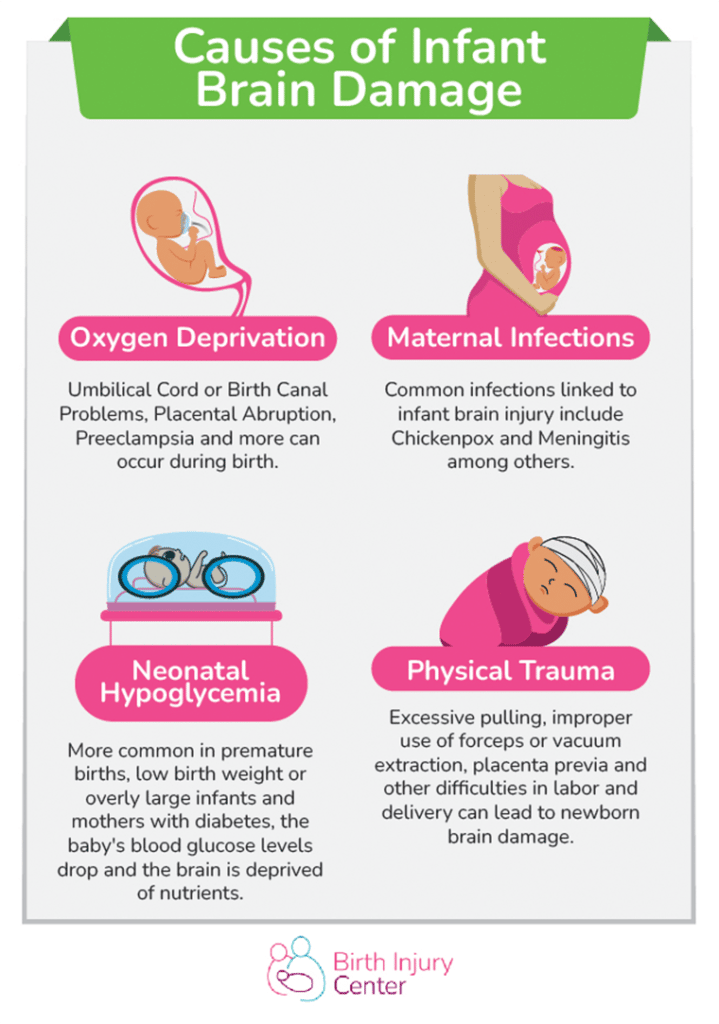
1. Oxygen Deprivation
During birth, the baby’s brain relies on a steady supply of oxygen to support its growth and development. If the baby’s oxygen supply is cut off or reduced for even a short period, it can cause brain damage. Oxygen deprivation can occur due to a variety of factors, including a compressed or twisted umbilical cord, placental abruption, or maternal high blood pressure.
In some cases, oxygen deprivation can be prevented by monitoring the baby’s heart rate and oxygen levels during labor and delivery. In other cases, emergency interventions such as a cesarean section or assisted delivery may be necessary to ensure the baby receives adequate oxygen.
2. Trauma During Delivery
Trauma during delivery can occur if the baby’s head is subjected to excessive force or pressure during labor and delivery. This can cause bleeding, swelling, or other damage to the brain. Trauma can occur due to a difficult delivery, incorrect use of delivery tools, or a large baby relative to the mother’s pelvis.
Preventing trauma during delivery requires proper monitoring of both mother and baby during labor, appropriate use of delivery tools, and timely interventions if complications arise.
3. Infections
Infections during pregnancy or delivery can lead to brain injury in the baby. Maternal infections such as rubella, cytomegalovirus, or toxoplasmosis can be transmitted to the baby and cause brain damage. Infections during delivery such as sepsis or meningitis can also cause brain injury.
Preventing infections during pregnancy and delivery requires proper prenatal care and monitoring, and appropriate use of antibiotics and other treatments as needed.
4. Premature Birth
Premature birth, or birth before 37 weeks of gestation, can increase the risk of brain injury in the baby. Premature babies may have underdeveloped brains or be more susceptible to oxygen deprivation or infections.
Preventing premature birth requires proper prenatal care and monitoring, and interventions such as bed rest or medication if preterm labor is detected.
5. Genetic Factors
Some genetic factors may increase the risk of brain injury at birth. For example, genetic disorders such as Down syndrome or fragile X syndrome can affect brain development and function. Inherited factors such as maternal or fetal blood clotting disorders can also increase the risk of brain injury.
Preventing brain injury due to genetic factors may not be possible, but appropriate monitoring and early interventions can help improve outcomes for affected children.
6. Maternal Health
Maternal health can also play a role in the risk of brain injury at birth. Maternal conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or preeclampsia can affect the baby’s growth and development, as well as increase the risk of complications during labor and delivery.
Preventing brain injury due to maternal health issues requires proper prenatal care and monitoring, and appropriate management of any underlying conditions.
7. Drug Use
Drug use during pregnancy can increase the risk of brain injury in the baby. Certain drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamine can cause blood vessel constriction and reduce oxygen supply to the baby’s brain. Other drugs such as alcohol or opioids can affect brain development and function.
Preventing brain injury due to drug use during pregnancy requires appropriate education, support, and interventions to help women avoid or overcome drug addiction.
8. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as exposure to toxins or pollutants can also increase the risk of brain injury at birth. For example, exposure to lead or mercury can affect brain development and function. Exposure to air pollution or cigarette smoke can also increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and delivery.
Preventing brain injury due to environmental factors requires appropriate education, support, and interventions to help women reduce their exposure to toxins and pollutants.
9. Lack of Access to Care
Lack of access to appropriate medical care during pregnancy and delivery can also increase the risk of brain injury at birth. Women who lack access to prenatal care or who give birth in settings with limited resources may not receive adequate monitoring, interventions, or treatment.
Preventing brain injury due to lack of access to care requires appropriate education, support, and interventions to help women access the care they need.
10. Other Factors
In some cases, brain injury at birth may occur due to unknown or uncontrollable factors. However, proper monitoring, interventions, and support can help improve outcomes for affected children.
In conclusion, understanding the causes of brain injury at birth is essential to preventing it from happening and improving outcomes for affected children. By addressing the various factors that can contribute to brain injury, healthcare providers, policymakers, and families can work together to promote healthy pregnancies, safe deliveries, and optimal outcomes for all children.
Frequently Asked Questions
Brain injury at birth is a serious medical condition that can have lifelong consequences. In this article, we will discuss the causes of brain injury at birth and answer some frequently asked questions about this condition.
What are the most common causes of brain injury at birth?
The most common causes of brain injury at birth include lack of oxygen, trauma during delivery, and infections. Lack of oxygen can occur due to a number of reasons, such as umbilical cord compression, placental abruption, or prolonged labor. Trauma during delivery can occur if the baby is too large, if the delivery is prolonged, or if the baby is in a difficult position. Infections such as meningitis or encephalitis can also cause brain injury at birth.
It is important to note that brain injury can occur during any stage of the pregnancy, but it is most common during the delivery process. In some cases, the cause of brain injury at birth may not be immediately apparent and may require further investigation.
What are the signs and symptoms of brain injury at birth?
The signs and symptoms of brain injury at birth can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some common signs and symptoms include seizures, difficulty breathing, poor muscle tone, and developmental delays. In severe cases, the baby may have difficulty feeding, may be unresponsive, or may have a decreased level of consciousness.
If you suspect that your baby may have suffered a brain injury at birth, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Early intervention and treatment can help improve the outcome and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
How is brain injury at birth diagnosed?
Brain injury at birth can be diagnosed through a variety of tests and procedures. The healthcare provider may perform a physical exam and order imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan to assess the extent of the injury. Blood tests may also be performed to check for infections or other underlying medical conditions.
In some cases, the healthcare provider may refer the baby to a specialist such as a neurologist or developmental pediatrician for further evaluation and treatment.
What are the treatment options for brain injury at birth?
The treatment options for brain injury at birth depend on the severity of the injury and the underlying cause. In some cases, the baby may require supportive care such as oxygen therapy, medication, or feeding support. Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy may also be recommended to help the baby reach their developmental milestones.
In more severe cases, surgery may be required to remove any blood clots or relieve pressure on the brain. Long-term care may also be necessary for babies with significant developmental delays or disabilities.
What is the long-term outlook for babies with brain injury at birth?
The long-term outlook for babies with brain injury at birth depends on the severity of the injury and the level of intervention and treatment. In some cases, babies may experience significant developmental delays or disabilities, while in other cases, they may make a full recovery with minimal long-term effects.
It is important for babies with brain injury at birth to receive early intervention and ongoing care to help them reach their full potential. Supportive therapies such as physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy can be highly effective in improving outcomes and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
In conclusion, the causes of brain injury at birth are numerous and complex. However, the most common causes include oxygen deprivation, traumatic delivery, and infections during pregnancy. Each of these factors can have a significant impact on the development of the baby’s brain and can result in long-term consequences.
Despite the severity of brain injuries at birth, there are steps that can be taken to prevent them. Prenatal care, including regular check-ups and monitoring for infections, can help identify and treat potential risks. Additionally, healthcare providers can take steps to minimize the risk of traumatic delivery by using techniques such as vacuum extraction or forceps only when necessary.
Ultimately, it is important for parents and healthcare providers to be aware of the causes and potential consequences of brain injury at birth. By being proactive in identifying and addressing risk factors, we can help ensure the health and well-being of newborns and their families.
Brenton Armour, the visionary founder and lead attorney at InjuryLawsuitHelper, boasts an impressive 15-year track record in personal injury law. His remarkable expertise spans cases from minor injuries to devastating accidents, earning him a sterling reputation as a trusted and passionate advocate for justice. Brenton's unwavering dedication to his clients has cemented his position as a sought-after personal injury attorney.
- Latest Posts by Brenton Armour
-
Can You Get A Misdiagnosis Cataracts?
- -
South Carolina Dog Bite Laws?
- -
Iowa Dog Bite Laws?
- All Posts